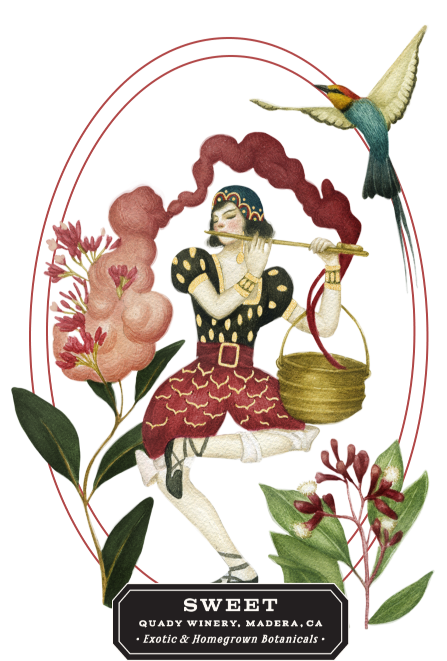
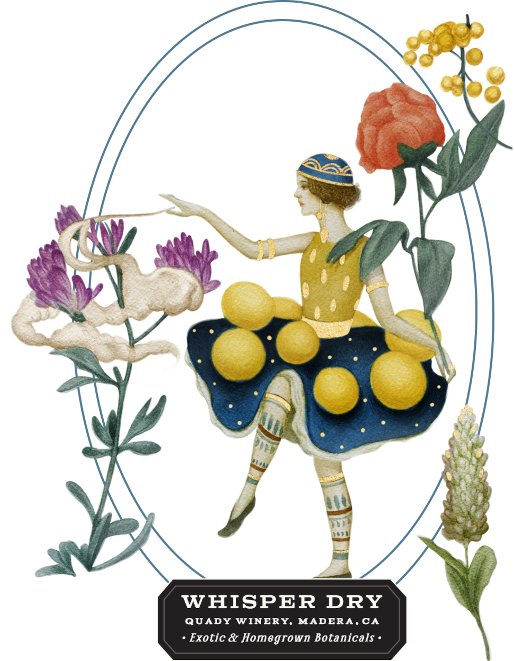
Herbs + Spices + Magic
Vya Apothecary
Vya was designed to be enjoyed like a fine wine: for flavor, aroma and complexity. Learn more about the botanicals that are infused into each vermouth.
Vya Botanicals
Alfalfa

Bitter Orange Peel

Cardamom
Cloves

Coriander Seed
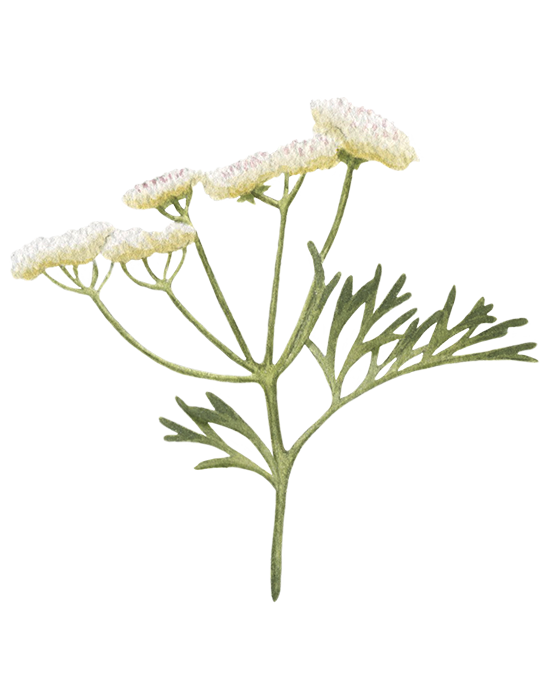

Elecampane Root
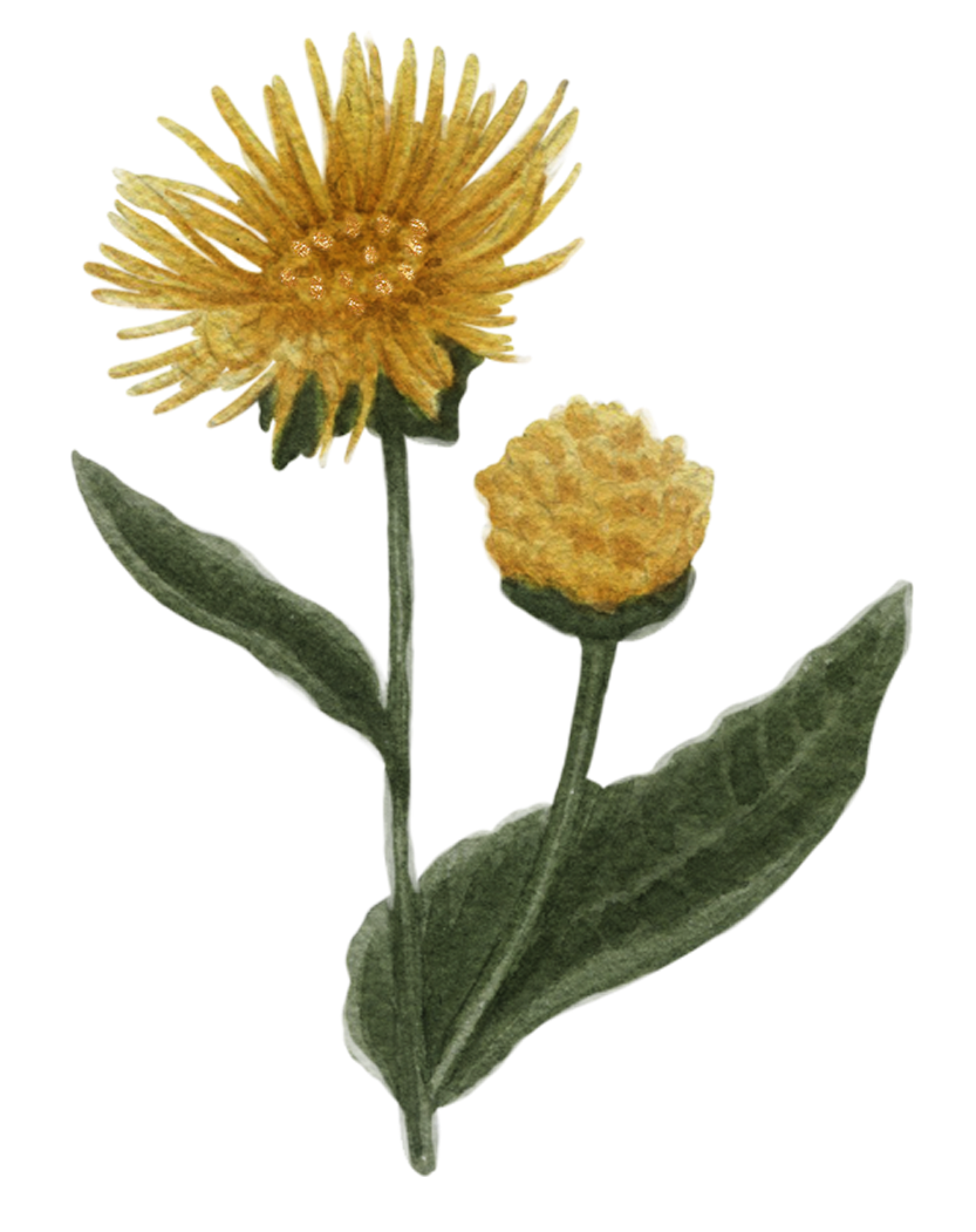

Galangal Root
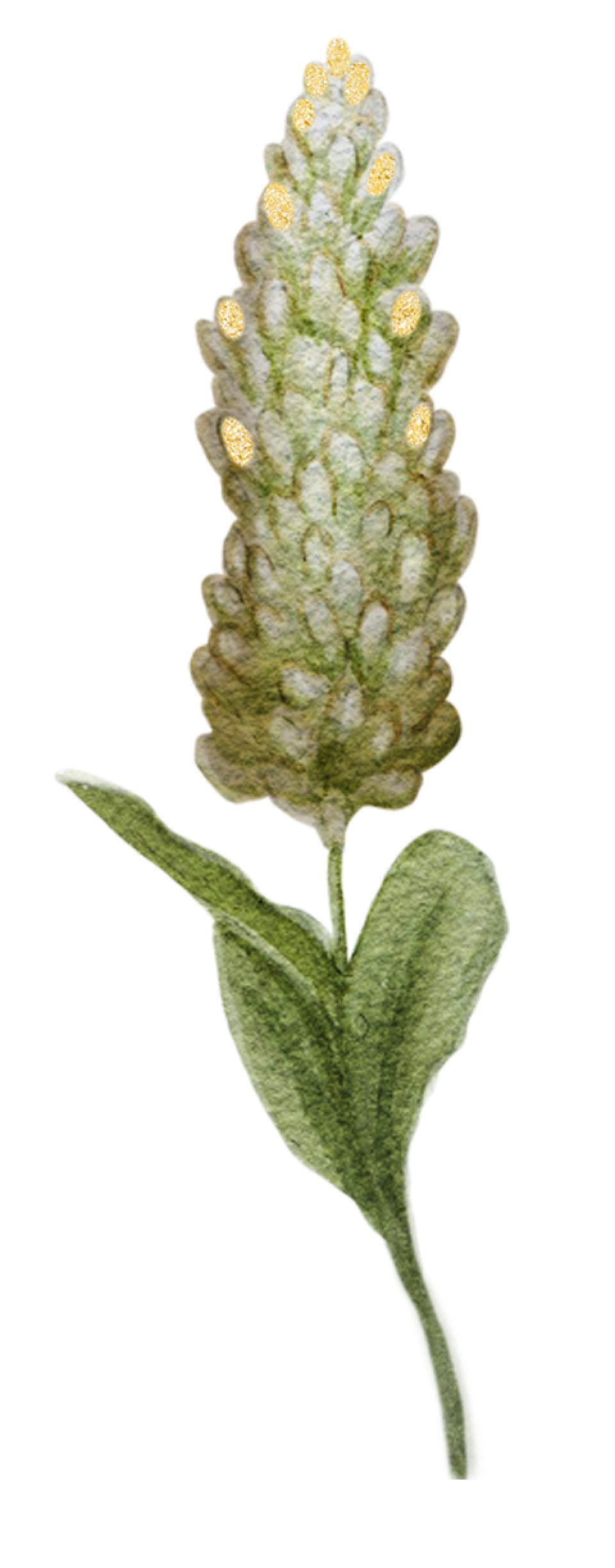

Lavender
Linden Flowers
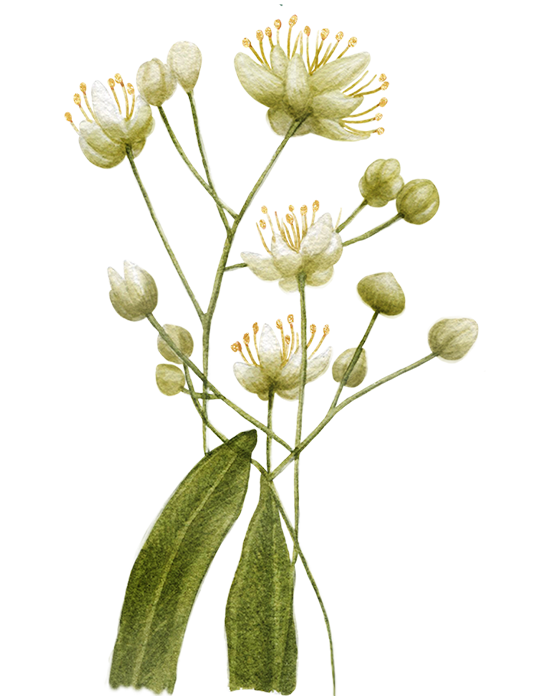

Orris Root

Quassia Bark

Red Clover

Rosebuds
Sage Leaf

Summer Savory

Sweet Orange Peel

Thyme

Angelica Root

Bitter Orange Peel

Blessed Thistle
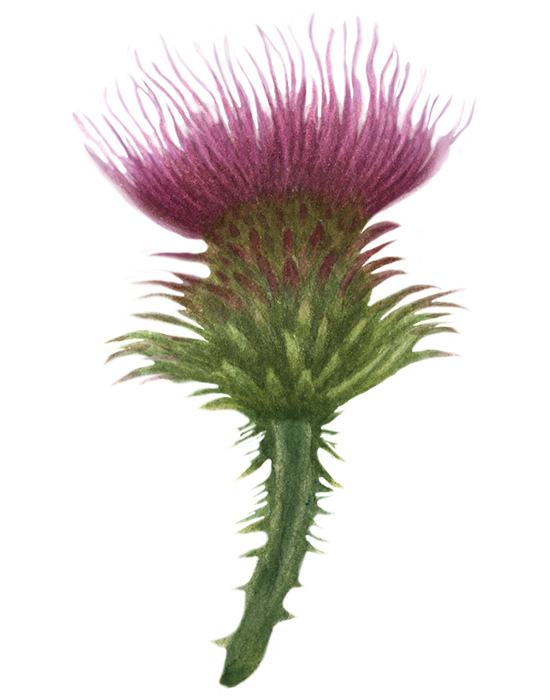

Cardamom

Cinchona Bark
Cinnamon
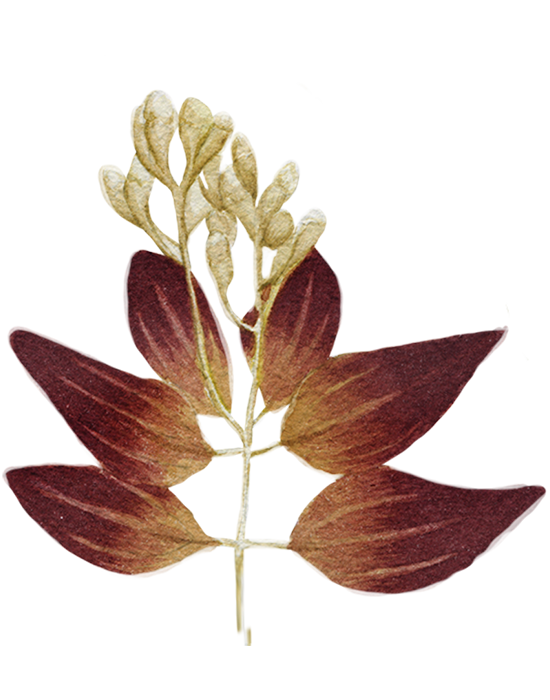

Cloves

Coriander Seed

Elecampane Root

Galangal Root

Gentian Root
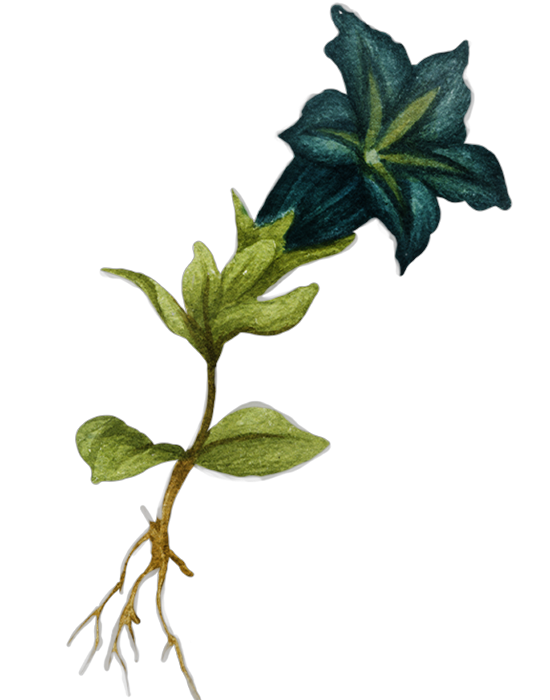

Nutmeg
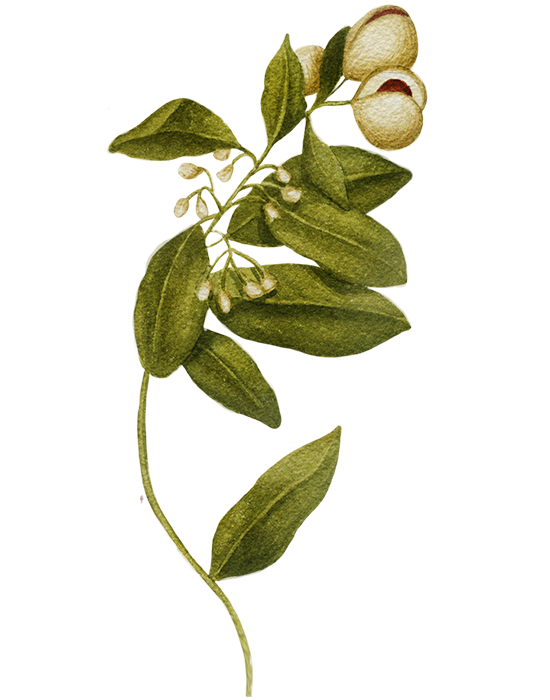

Quassia Bark

Sweet Orange Peel

Alfalfa

Balsam Fir Needles

Bitter Orange Peel

Cardamom

Cloves

Coriander Seed

Elecampane Root

Galangal Root

Lavender

Linden Flowers

Orris Root

Quassia Bark

Red Clover

Rosebuds
Sage Leaf

Summer Savory

Sweet Orange Peel

Thyme


FOUNDATIONS
The Wines in Vya
Vya is more than just botanicals! The proprietary base wines we use also set us apart from other vermouths and add to the rich complexity found in every bottle.
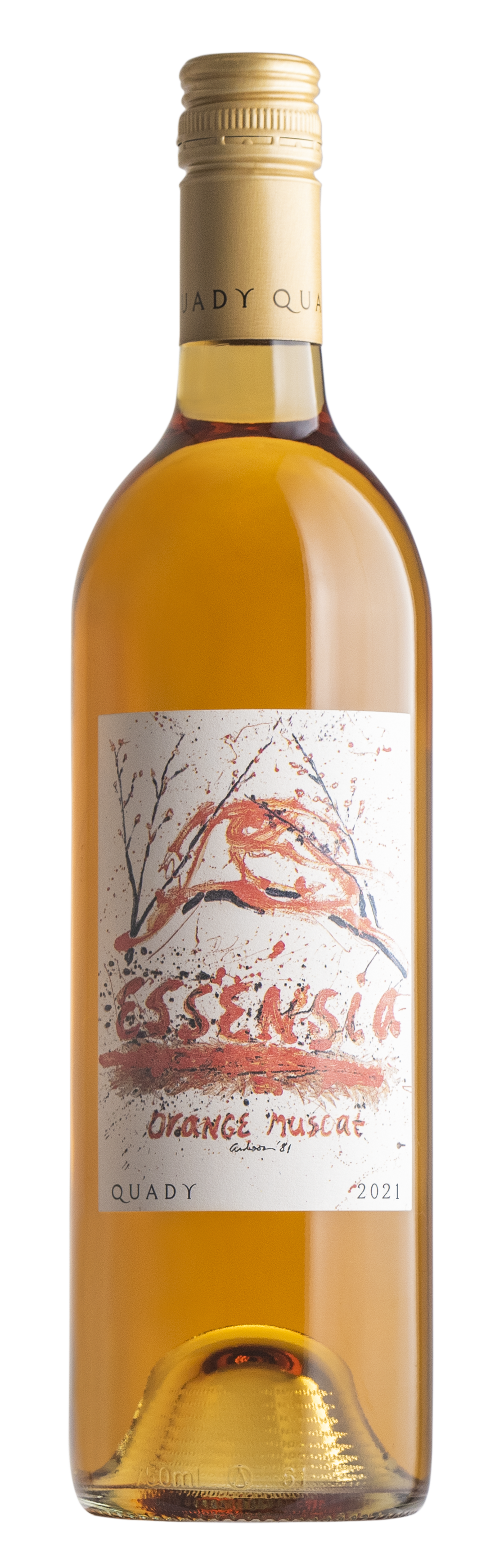

Essensia Orange Muscat
Made from the distinctive, lesser used Orange Muscat variety, Essensia was created by Andrew Quady in 1980 and opened new premium categories in the American wine industry upon its release. During Essensia’s fermentation process, the juice is allowed to soak with the skins of the grapes, enhancing its flavors and honey-gold color with the very essence of the Orange Muscat grape. With its orange-marmalade characteristics, Essensia is blended into each Vya Vermouth (in different quantities) to add viscosity, aroma, texture and complexity. The addition of Quady’s proprietary Essensia Orange Muscat wine is unique to Vya and cannot be experienced with any other vermouth.

Vya Sweet

Vya Whisper Dry
Vya Extra Dry

Starboard Batch 88
Starboard Batch 88 is a port-style wine made by Quady Winery using the same grape varieties – Tinta Roriz – and methods as in the Duoro River Valley in Portugal, where port is traditionally crafted. However, the San Joaquin Valley climate is warmer with different soils, and the Tinta Roriz vineyards here produce loose bunches and a small crop. Therefore, we blend different vintages – each with an average age of 5 years – into one decadent, smooth wine with rich chocolate-raisin character that’s halfway between a ruby and a tawny. Starboard is blended into Vya Sweet, along with Essensia, to add flavor, viscosity, aroma, texture and complexity. The addition of Quady’s proprietary Starboard Batch 88 port-style wine is unique to Vya Sweet and cannot be experienced with any other vermouth.

Vya Sweet

Dry California White Wine
All vermouths start with a base of dry white wine. In Vya, we look for a fresh, clean, neutral wine that can act as a carrier for the botanicals, the Essensia, and the Starboard, without interference. The dry white wine allows the more spectacular components of Vya to shine.

Vya Sweet
Vya Extra Dry

Vya Whisper Dry
RESILIENCY
The Road to Sustainability
Quady Winery became CSWA Certified Sustainable in 2022. We’re strategizing and taking steps to continue to do better.